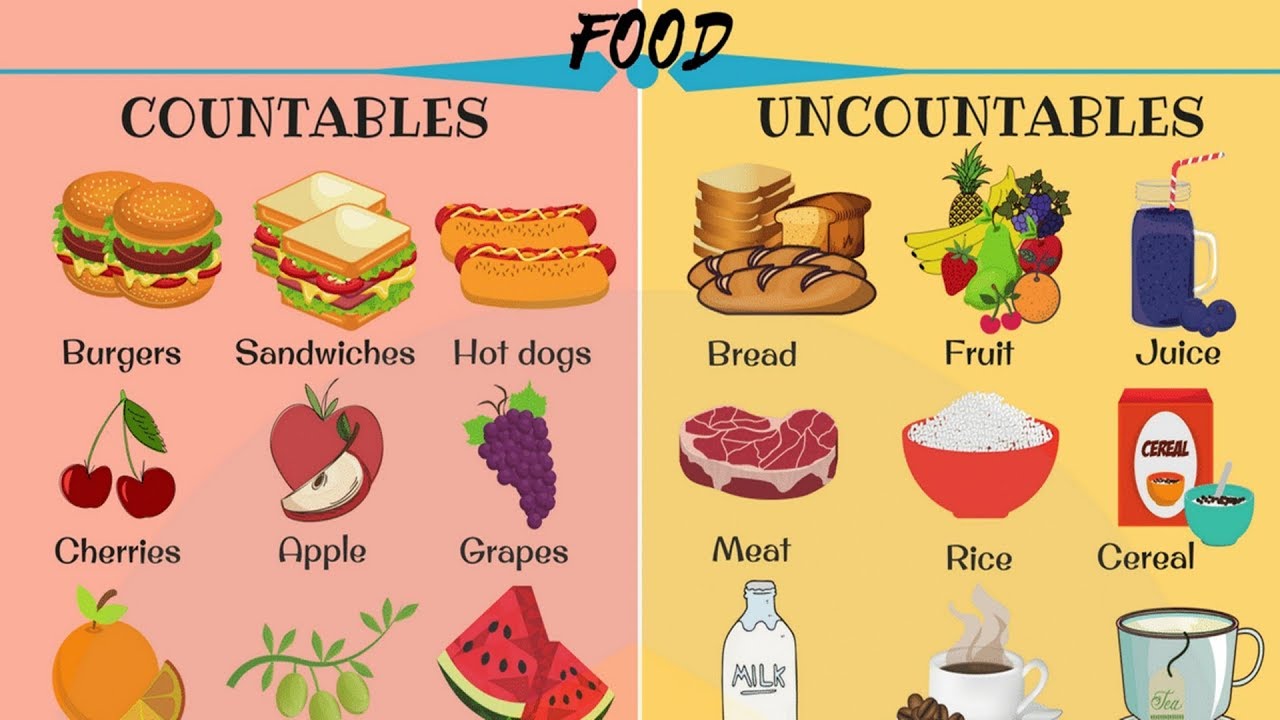
In Grammar Unit 1.3, we learnt about singular and plural nouns. This concept is important when learning about countable and uncountable nouns. Let’s first begin by understanding countable and uncountable nouns.
Countable Nouns
Countable nouns are nouns that can easily be counted such as apples, people, cars, dogs and trees etc. If you can count them, they are called countable nouns. For example:
- one apple
- two people
- four cars
- eight dogs
- sixteen trees
Uncountable Nouns
Uncountable nouns are nouns that cannot be easily counted. You have to measure them using something or you might have difficulty using a number to represent the nouns. I like to tell my students that uncountable nouns are nouns that you cannot hold properly with your hands. These nouns will easily slip through your fingers, such as sand, water, and air. A lot of times, uncountable nouns are too small to be counted or cannot be seen with your eyes. For example:
- sand
- water
- air
- fun
- love
- anger
- food
- homework
- paper (paper is counted in sheets – one sheet of paper, two sheets of paper etc. You don’t say “one paper” or “two papers”.)
Applying Singular and Plural Nouns
Countable nouns can be singular or plural. If you only have one, it is singular. If there are more than one, they are plural. For example:
- 1 apple (singular) / 2 apples (plural)
- 1 person (singular) / 4 people (plural)
- 1 car (singular) / 8 cars (plural)
- 1 dog (singular) / 16 dogs (plural)
- 1 tree (singular) / 32 trees (plural)
Uncountable nouns are always considered to be singular. Also, uncountable nouns are measured instead of counted. If we want to count them, we count using something else. For example:
| Noun | We don’t say | Instead, we say |
| Water | 1 water | 1 litre of water / 1 bottle of water etc. |
| Salt | 2 salts | 2 teaspoons of salt / 2 bags of salt etc. |
| Rice | 3 rices | 3 kilograms of rice / 3 bowls of rice etc. |
| Sand | 4 sands | 4 bags of sand / 4 boxes of sand etc. |
| Milk | 5 milks | 5 cups of milk / 5 cartons of milk etc. |
Quantifiers
Quantifiers can be used for countable and uncountable nouns. We use quantifiers when it is difficult or when we are lazy to count/measure. For example, maybe you might be too lazy or have no time to count the number of people at your birthday party. So you use a quantifier to say whether you have a lot of people or not.
Sometimes it is difficult to count or measure a noun because there is/are a lot of that noun. When there is or there are a lot of a noun, we say many or much.
| Countable Nouns | Uncountable Nouns | |
| A lot of | many | much |
| NOT a lot of | few | little |
Countable Nouns
- a lot of children = many children
- a lot of cats = many cats
- a lot of flowers = many flowers
- a lot of stones = many stones
- a lot of houses = many houses
- NOT a lot of people = few people
- NOT a lot of animals = few animals
- NOT a lot of trees = few trees
- NOT a lot of shops = few shops
- NOT a lot of classrooms = few classrooms
Uncountable Nouns
- a lot of water = much water
- a lot of food = much food
- a lot of sand = much sand
- a lot of love = much love
- a lot of anger = much anger
- a lot of air = much air
- a lot of sugar = much sugar
- NOT a lot of oil = little oil
- NOT a lot of strength = little strength
- NOT a lot of time = little time
- NOT a lot of money = little money
- NOT a lot of energy = little energy
- NOT a lot of joy = little joy
- NOT a lot of salt = little salt
Examples of Countable and Uncountable Nouns
Below is a short list of countable and uncountable nouns.
| Countable Nouns | Uncountable Nouns |
| Apartment | Kindness |
| Bicycles | Light |
| Country | Money |
| Doctor | Noise |
| Elephant | Oil |
| Factory | Paper |
| Garden | Quality |
| House | Rubbish |
| Implant | Sorrow |
| Jacket | Time |
Other Quantifiers
There are other quantifiers, which can be used for both countable and uncountable nouns. Here are some examples:
- some
- any
- all
- no
- more
- most
- enough
- less
- lots of